Moxibustion

Moxibustion
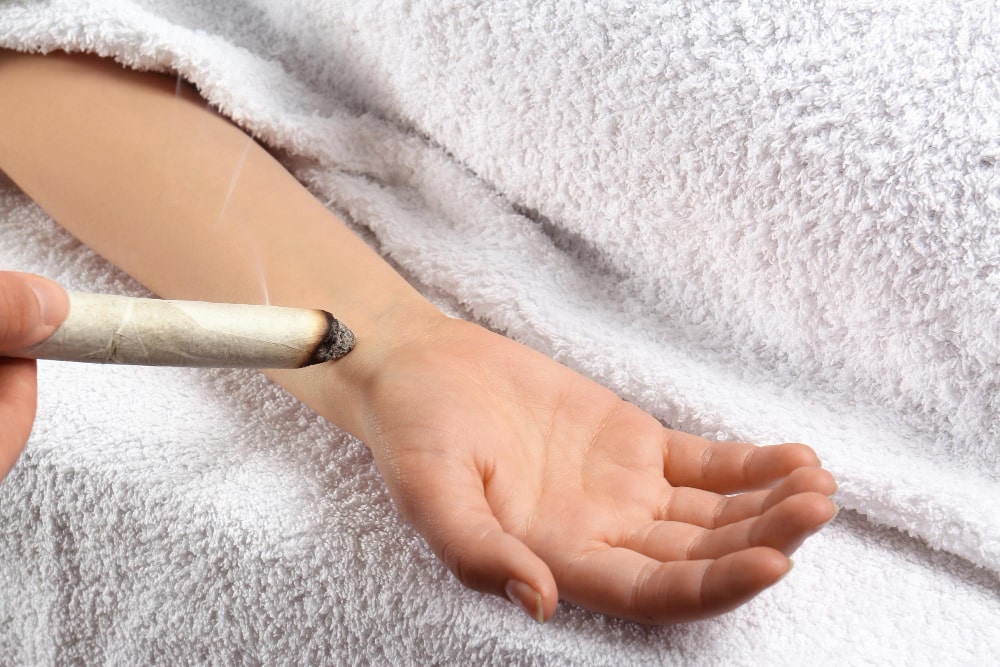
Moxibustion is an ancient Chinese heat therapy used in Traditional Chinese Medicine. A dried herb called mugwort (artemisia vulgaris), also known as “moxa”, is burned on or near the surface of the skin along acupuncture points in order to warm and stimulate the channels of the body. Burning moxa produces a strong smell similar to the smell of marijuana.
There are many forms of moxibustion techniques. The most common technique is when a practitioner holds a burning moxa stick above the surface of the skin moving it along acupuncture meridians and points, muscle groups, and joints. Sometimes a practitioner will place moxa directly on the acupuncture needle in order to facilitate a deeper warming effect. This heat therapy warms the body, stimulates circulation of stagnated blood and qi in the meridians, boosts the immune system, and dispels pathogens.
Moxibustion treats a variety of pain conditions such as arthritis, digestive ailments, tendonitis, joint swelling, muscle stiffness, menstrual cramps, migraines, and helps with breech pregnancy. This practice is safe and effective especially when paired in conjunction with acupuncture treatments. Patients report a feeling of warmth and a relaxing sensation.

